Phase 3 Environmental Sites Assessment
Phase III assessments include additional intrusive testing and a plan to mitigate environmental issues based on the results of the previous assessments. During this phase, the size and source of the contamination will be characterized through methods such as installation of ground water monitoring wells.
A Phase III ESA is conducted when a release of polluting substances is detected during a Phase II ESA*, and it includes additional testing to determine the extent and magnitude of the release. Once the scope and magnitude of a release are determined, the data is compared to applicable regulatory criteria and other requirements to determine whether remediation of the impacted environmental matrices is indicated.
What is a Phase III ESA?
A Phase III Environmental Site Assessment (ESA), also known as a remedial investigation or feasibility study, is yet another crucial step in environmental due diligence when conducting a property transaction or when developing a property that requires remedial action.
Phase III assessments include additional intrusive testing and a plan to mitigate environmental issues based on the results of the previous assessments. During this phase, the size and source of the contamination will be characterized through methods such as installation of ground water monitoring wells.
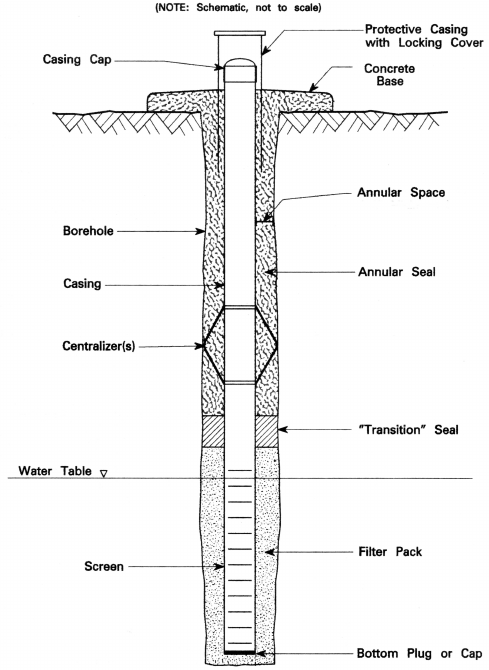
Temporary groundwater monitoring wells or sampling points are generally installed in boreholes driven by direct push technology (DPT). After completion of the borehole, a well casing consisting of a solid riser, well screen, and bottom cap is inserted into the borehole. A filter pack may or may not be installed.
What is a groundwater monitoring well?
Groundwater monitoring wells are principally used for observing groundwater levels and flow conditions, obtaining samples for determining groundwater quality, and for evaluating hydraulic properties of water-bearing strata. Monitoring wells are sometimes referred to as "observation wells."
Monitoring wells are designed to monitor groundwater to evaluate the changes in the physical, chemical and biological properties of water. To be effective, groundwater monitoring wells installation should be done in such a way that the properties of the groundwater samples are not affected.
The planning and the execution of a remediation of an impacted site
Generally, a Phase III Environmental Sites Assessment (ESA) is the term used to describe the contaminated site remediation phase of an ESA. This includes both the planning and the execution of a remediation of an impacted site.
RSK believes that each unique site deserves a tailored approach to remediation. RSK team relies on proven, industry-leading environmental remediation strategies and technologies that are solutions-focused, meaning that the client’s goals for the site are the foundation of the remediation approach. RSK also works to reduce the amount of soil sent to landfills by using on-site testing tools to delineate the exact limits of the impacted zone, instead of relying on best guesses, and by working within the regulation to allow some soil to remain on site, where appropriate. This saves money for the client and is more environmentally sustainable.